Describe the Response to the Plantar Stimulation Use Appropriate Terminology
There is positive response to 507 monofilament at the dorsal foot negative response on the plantar foot. When the knee is tapped the nerve that receives this stimulus sends an impulse to the spinal cord.
The Babinski reflex also called the plantar reflex is commonly tested soon after birth and during routine wellness check-ups.
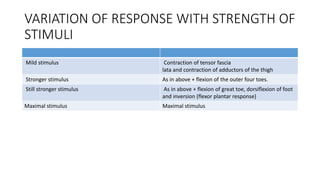
. In some patients stroking the sole produces extension dorsiflexion of the big toe often with extension and abduction fanning of the. A normal positive response usually involves a contraction of the abdominal muscles at the side of the stimuli and the umbilicus moving towards the source of the stimulation. The term voluntary suggests that there is a conscious decision to make a movement.
Often there is also flexion and adduction of the other toes. A reflex is built into the nervous system and does not need the intervention of conscious thought to take effect. The plantar response because the sole is the plantar surface of the foot the toe or big toe sign or phenomenon and the Babinski reflex response or phenomenon.
The term voluntary suggests that there is a conscious decision to make a movement. In adults stimulation of cutaneous receptors in the sole of the foot as when testing the plantar reflex usually causes the toes to flex and move together. Associated responses include lacrimation and miosis.
Clonus is involuntary and rhythmic muscle contractions caused by a permanent lesion in descending motor neurons. When the sole of the foot is stimulated along with the outside of sole towards the toe the normal response is flexion of the great toe with flexion of other toes. The knee jerk is an example of the simplest type of reflex.
Stretch reflexes are important for maintaining and adjusting muscle tone for posture balance and locomotion. Somatic senses inform the nervous system about the external environment but the response to that is through voluntary muscle movement. Describe the positive Babinski sign reflex.
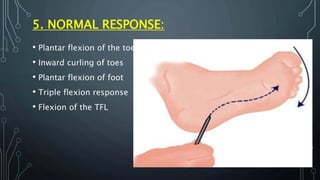
This normal response is termed the flexor plantar reflex. There is pitting edema on the lower extremity to the knee. This reflex happens when the sole of the foot is stimulated with a blunt instrument.
These reflexes aid newborns to survive while they have limited control over their body. These also provide health clues which is why assessment of the neuromuscular function is part of the general newborn examination. Stroking the lateral part of the sole of the foot with a fairly sharp object produces plantar flexion of the big toe.
It is present or absent. However some aspects of the somatic system use voluntary muscles without conscious control. TheBabinski sign indicating an upper motor neuron lesion is characterized by extension of the great toe and fanning of the remaining toes.
In general clonus may occur in any muscle with a frequency of 5-8 Hz and the average period of oscil. Describe the response to the plantar stimulation. Blinking in response to a threat or to tactile stimulation of the cornea as for example when measuring objectively the corneal touch threshold.
Stimulation of the sole of. The authors describe the performance of acceleromyography and the need for initial calibration when using these quantitative devices. They utilize neurons of the autonomic nervous system to elicit their actions.
When a foot bends upward at the ankle this movement is known as. Clonus may be found at the ankle patella triceps surae wrist jaw biceps brachii. Visceral reflexes involve a glandular or non-skeletal muscular response carried out in internal organs such as the heart blood vessels or structures of the GI tract.
Too vigorous stimulation may produce withdrawal which may be misinterpreted as a. Electrodes correctly and to use appropriate sites for nerve stimulation as well as appropriate stimulation patterns. Specific focus should be given to newborns alertness muscle tone and strength head control and response to.
Somatic senses inform the nervous system about the external environment but the response to that is through voluntary muscle movement. The term myoparesis is used to describe. Few reflexes are monosynaptic one synapse and involve only two neuronsone sensory and one motor.
Nociceptive input travels up the tibial and sciatic nerve to the S1 region of the spine and synapse with anterior horn cells. The plantar reflex deserves special attention. The Babinski reflex also called the Babinski sign or plantar reflex is an automatic reflex in the foot in.
A doctor will use a blunt object to test the Babinski reflex. However with wide base of support minimal heeltoe sequence and lateral trunk sway. Gait is independent without assistive device.
A reflected action or movement. The toes curl down and inward. Reflexes can either be visceral or somatic.
Plantar reflex is polysynaptic and elicited by cutaneous stimulation rather than stretch b. Some of the newborn reflexes. Use appropriate terminology b.
Achilles tendon reflexes are diminished. The plantar response is obtained by stimulation of the lateral aspect of the sole of the foot beginning at the heel and extending to the base of the toes. In adults stimulation of cutaneous receptors in the sole of the foot as when testing the plantar reflex usually causes the toes to flex and move together.
Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic diseases characterized by progressive weakness and degeneration of the skeletal muscles. The plantar reflex is a superficial spinal reflex that depends both on functional upper-level motor pathways and on the cord-level reflex arc. The plantar reflex is a superficial spinal reflex that depends both on functional upper-level motor pathways and on the cord-level reflex arc.
The second part focuses on current developments and ongoing discussion. The response results from nociceptive fibers in the S1 dermatome detecting the stimulation. Image formed by reflection of light from the cornea Fig.
It assesses normal development and may offer an early indication of developmental issues. Since there is a delay in the impulse at synapses the more synapses in a reflex arc the slower the response. Interestingly the response is different between.
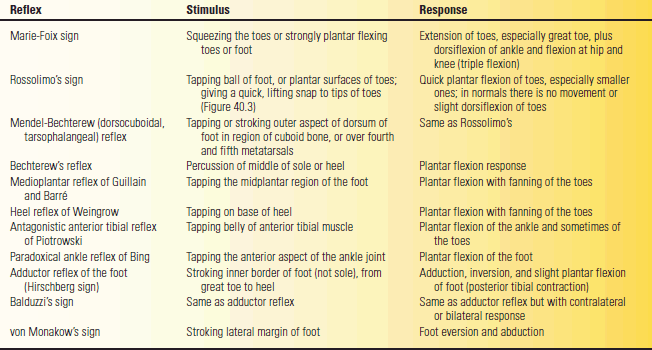
While a response similar to the sign exists when the plantar reflex is elicited in infants Presence of Babinskis sign in adults can be indicative of a lesion or damage in the corticospinal tract and identification of the sign remains one of the. Stimulate the sole of your partners foot by moving the handle of the reflex hammer along the outside of the sole towards the toes. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events CTCAE - Glossary Report Bethesda Maryland 20892 5 of 34 -- B --Babinski sign banding baseline blood patch BMD BMI BP BSA bullae An abnormal reflex consisting of dorsiflexion of the great toe and abduction of the other toes in response to cutaneous stimulation of the plantar surface of the foot.
Use appropriate terminology. The sum total of any particular automatic response mediated by the nervous system. However some aspects of the somatic system use voluntary muscles without conscious control.
The Babinski sign is known by a number of other names. Babinskis sign is observed when the Hallux big toe exhibits dorsal extension in response to the same plantar stimulation. It is common but wrong to say that the Babinski sign is positive or negative.
The motor response which leads to the plantar flexion is mediated through the S1 root and tibial nerve. Weakness or slight muscular paralysis. The Babinski reflex is relatively easy to test at home and with little training.
Pathologic Reflexes Neupsy Key

Solved Plantar Reflex Stimulale The Sole Of Your Partner Foot By Moving The Handle Of The Reflex Hammer Along Ihe Outside Of The Sole Towards The Toes Note If You Do Not Have





No comments for "Describe the Response to the Plantar Stimulation Use Appropriate Terminology"
Post a Comment